Useful information about the taxon (species, subspecies, variety...)
Ulmus laevis Pall. 1784
Ulmaceae
(APG IV)European white elm
Taxon concept: The Plant List (2014), version 1.1
Distribution: Europe without the British Isles, Iberian Peninsula; Turkey; Caucasian States
Ulmus laevis Pall. - Accepted: Ulmus laevis Pall. bei The Plant List (2010); Familie: Ulmaceae (APG III)Ulmus laevis Pall. - Accepted: Ulmus laevis Pall. bei The Plant List (2014), version 1.1; Familie: Ulmaceae (APG III)Ulmus laevis Pall. - Accepted: Ulmus laevis Pall. bei BfN Checklist Flora DE; Familie: Ulmaceae (APG IV)
- Difference to related species
- is less affected by the Dutch elm disease than other elm tree species
- Flowers
- hermaphrodite
- Flower ecology
- wind-pollinated (anemophilous)
- Life form
- woody, tree
- Leaves
- leaves with 2 cm long stems
- Foliage persistence
- deciduous
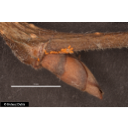
- Fruits
- ovate samara with central seed and a hair-fringed wing margin
- Fruit ecology
- wind-dispersed (anemochorous) or water-dispersed (hydrochorous)
- Soil conditions
- preferentially on perculating wet, temporarily flooded, nutrient-rich and alkaline, humus-rich, sandy or pure loam and clay soils
- Root type
- deep-rooting plant with formation of buttress roots
- Natural occurrence (habitat)
- bottomland riparian forests
- Vegetation typ and synecology (plant community)
- temperate, mixed mesophytic broad-leaved deciduous forests
- Life span
- to 250 years old
- Usage
- used as an ornamental and urban tree; wood can be used as a fuel
Erhardt, W., Götz, E., Bödeker, N. & Seybold, S. (2008): Der große Zander. Enzyklopädie der Pflanzennamen. Band 2. Arten und Sorten. Eugen Ulmer KG, Stuttgart (Hohenheim), 18. Aufl., 2103 S.; Haider, M. et al. (2005): Wildbienenkataster. See: https://www.wildbienen-kataster.de; Schick, B. & Spürgin, A. (1997): Die Bienenweide. Eugen Ulmer Verlag, Stuttgart, Auflage: 4., völlig neubearb. u. erw. A., 216 S. 978-3800174188.; Westrich, P. et al. (2018): Die Wildbienen Deutschlands.. Ulmer Verlag ISBN 978-8186-0123-2.;
Diese Webseite verwendet Google Maps, um Karten und Standorte von Pflanzen in den Hohenheimer Gärten anzuzeigen. Dadurch werden unter Umständen Daten an Google weitergeleitet, was mit einer Verarbeitung Ihrer personenbezogenen Daten verbunden sein kann. Die Datenschutzerklärung von Google finden Sie hier: Datenschutzerklärung von Google
| Sex | Standort | Accession number | Planting year | Donation | IPEN | Lat. | Long. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parzelle K | EG-K-018-19669 | 1860 | XX-0-HOH-EG-K-018-19669 | 48,7091699499 | 9,2089842959 | ||
| Parzelle K | EG-K-106-19670 | 1860 | XX-0-HOH-EG-K-106-19670 | 48,7091444733 | 9,2090541528 | ||
| Parzelle Z | LG-Z-029-19668 | 2003 | + | XX-0-HOH-LG-Z-029-19668 | 48,704857242 | 9,2128605184 | |
| Parzelle N | SP-NB-069-10261 | XX-0-HOH-SP-NB-069-10261 | 48,7114199582 | 9,2165429664 | |||
| male and female flowers on the same individual | Parzelle N | SP-NB-077-16361 | 1999 | XX-0-HOH-SP-NB-077-16361 | 48,7113665222 | 9,2167739669 |